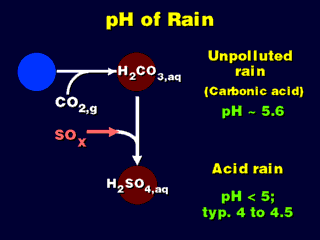
 Note that naturally occurring CO2 in the atmosphere dissolves in
rainwater and makes it slightly acidic (this will be the background, "natural"
acidity of rain). Any pH much lower than this (5.6)
is considered "acid rain". The acid in acid rain may be sulfuric or
nitric acid or a combination of both.
Note that naturally occurring CO2 in the atmosphere dissolves in
rainwater and makes it slightly acidic (this will be the background, "natural"
acidity of rain). Any pH much lower than this (5.6)
is considered "acid rain". The acid in acid rain may be sulfuric or
nitric acid or a combination of both.
The extreme cases of acid fog occur when the fog droplets are
evaporating, or the fog is "burning off". Evaporation of the droplets
reduces their size, but the acid gets left behind in the smaller droplet.
This causes the acid to become more concentrated, so the lowest pH (most
highly concentrated acid) occurs just as the fog "lifts".



 Note that naturally occurring CO2 in the atmosphere dissolves in
rainwater and makes it slightly acidic (this will be the background, "natural"
acidity of rain). Any pH much lower than this (5.6)
is considered "acid rain". The acid in acid rain may be sulfuric or
nitric acid or a combination of both.
Note that naturally occurring CO2 in the atmosphere dissolves in
rainwater and makes it slightly acidic (this will be the background, "natural"
acidity of rain). Any pH much lower than this (5.6)
is considered "acid rain". The acid in acid rain may be sulfuric or
nitric acid or a combination of both.